
Plastic Blow Molding
Quick Glance
Unit Cost
Surface Finish
Tolerance
Cost of capital investment
Production volumes
Possible geometries
Including injection blow molding, extrusion blow molding, and rotary wheel blow molding, a great process for making parts with internal voids such as bottles and ice packs.

Injection Stretch Blow Molding:
Similar to a glass blowing in concept but on an industrial level. Injection blow molding starts with an injection molded preform blank that often looks similar to a small test tube. The preform is heated and placed into a mold where a core rod stretched the preform as pressurized air is added. The material will expand to the wall of the mold and take up its shape. The mold will then pull apart and the part is removed.

Extrusion Blow Molding:
Extrusion Blow Molding uses a continues heated extrusion of material often shaped like a pipe and called a parison. The parison flows downward into a mold where it is clamped in and compressed air is fed inside the mold to press it against the inner walls of the mold to take its shape. After the mold is sufficiently cooled the mold is released and the excess is trimmed from the product and recycled.

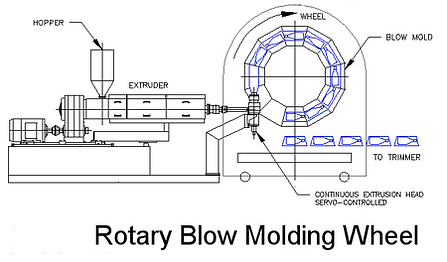
Rotary Wheel Blow Molding:
Using the same basic principle as Extrusion Blow Molding, Rotary Wheel Blow Molding produces parts continuously and at a huge scale. Instead of a single mold or shuttle of molds, a massive wheel of molds is used to continuously take the feed from the extruder, clamp it in a mold, inflate the part, and eject the part before cycling back to the extruder to make another. This is one of the largest forms of production with very large capital investments but capable of producing parts at a massive scale continuously. Often used for medium sized products with large quantities such as motor oil containers.
Multi-Layer Co-Extrusion Blow Molding:
Co-extrusion blow molding is a method of creating a multilayer part in order to achieve desired chemical or physical properties. It closely resembles extrusion blow molding except for additional layers of extrusions are added to the same part. Adhesive layers of often required to bind the materials together and prevent separation during the product's life. This is common for bottles and chemical containers that need a specialized inner layer exposed to the contents and a more durable and UV resistant outer layer.

Applicable Material:
Blow Molding offers a large variety of materials to use as well as multilayer walls for additional properties.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Medium & Low-Density Polyethylene (MDPE & LDPE), Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), Polypropylene (PP), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE), Polystyrene (PS), Polycarbonate (PC), Fluoropolymers (PTFE), Polyimide/Nylon
Advantages:
Fast cycle times
Low unit costs
Can make hollow products with threaded necks
Multi-Layer Co-Extrusion make for highly engineered containers
Injection Blow Molding allows bases of products to be reinforced with extra material
Disadvantages:
High Capital Costs
Require large amounts of floor space
Difficulty in regulating wall thickness with Extrusion Blow Molding
Example Products:
Nearly all hollow bodied plastic parts with a few exceptions that might be made with Rotomolding or a multistage process. Sizes range from small pill bottles to large 200-liter drums and structural paneling.
Bottles, barrels, protective casings, ornamental decorations, ice packs, gas cans, construction safety gear, etc.


.png)